For the second part of this chapter, I will explain the sharing of active infrastructures, from DAS sharing to RU sharing, related to wireless transmission and control components.
Active Infra-Sharing requires higher technological level
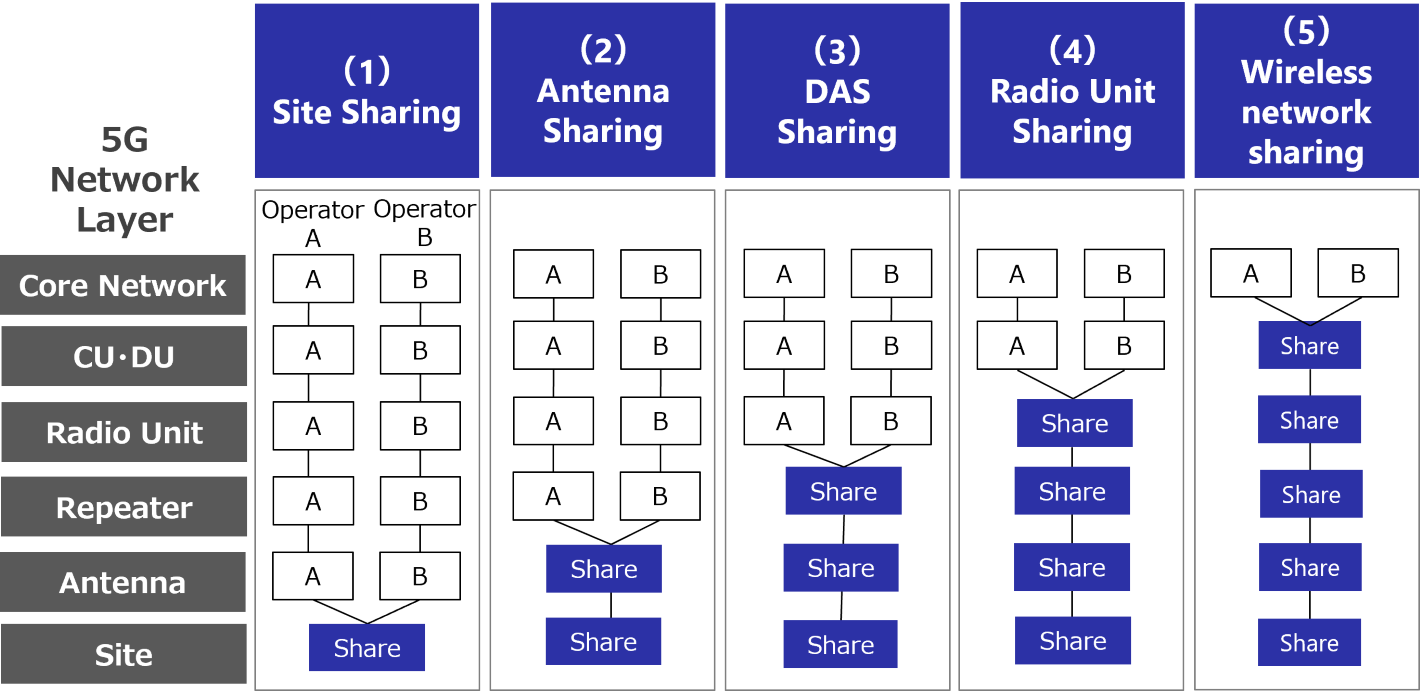
In the previous section, I focused on the range of sharing and introduced (1) Site sharing and (2) Antenna sharing as unrelated categories for transmission and control parts of wireless communication networks.
DU(Distributed Unit):Functional units for processing wireless signals and integration of RU
RU(Radio Unit):Functional units for controlling the transmission and reception of radio waves
In this section, I will cover from (3) DAS sharing to (5) Wireless network (CU/DU) sharing. These types of Infra-Sharing require high level of quality to provide the mobile communication networks without any problems. So, technical difficulty increases compared to Site sharing and Antenna sharing.
(3) DAS sharing
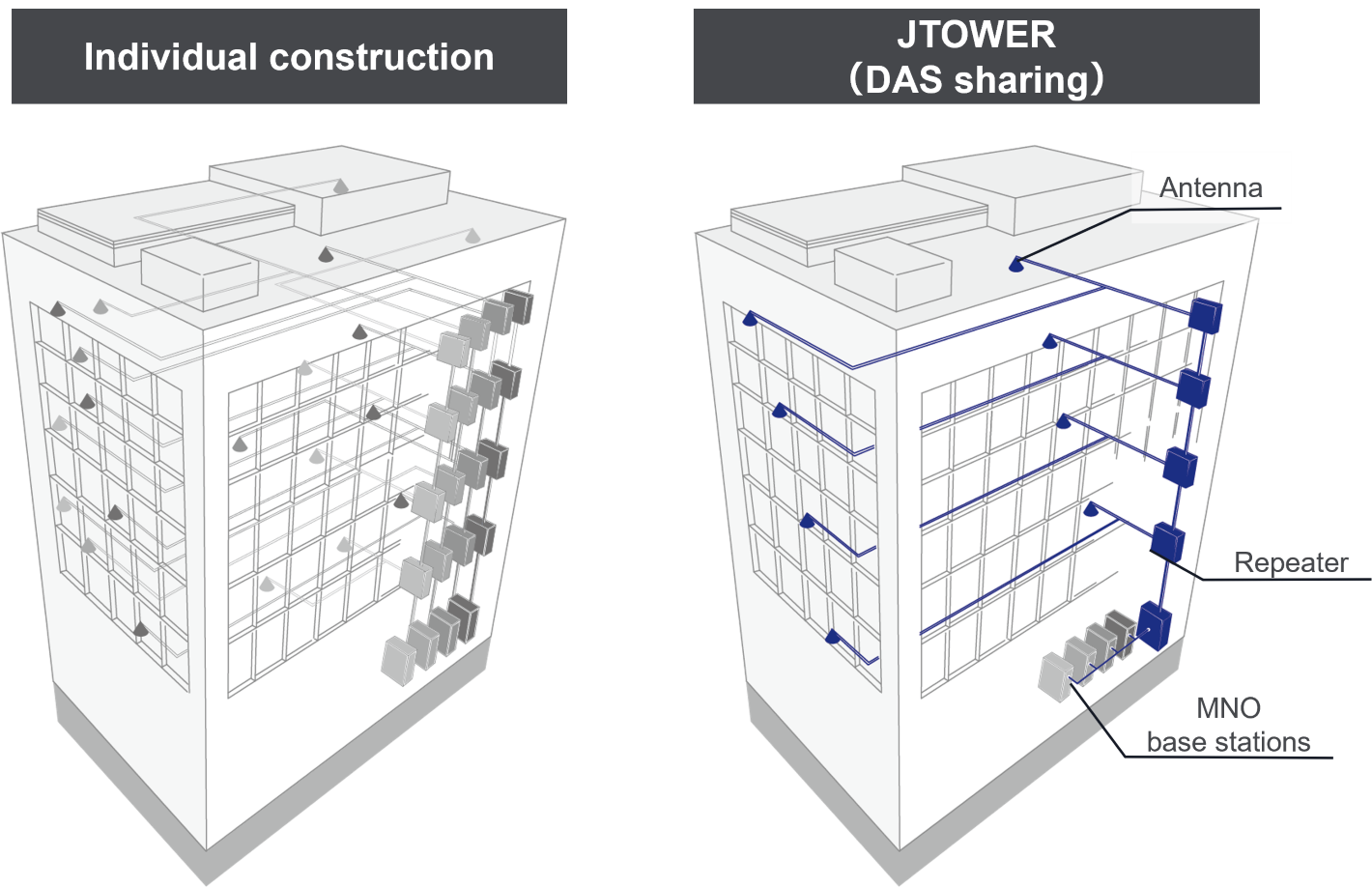
DAS sharing is mainly used for the indoor coverage in large-scale buildings such as offices and commercial facilities. In the large-scale buildings, radio wave from outside base station does not penetrate inside sufficiently, and the usage environment for mobile phone users is deteriorated. To improve the coverage, multiple antennas are distributed on each floor through the relay unit which transmits radio waves to various locations in the building by placing them optical fibers, and that requires considerable cost. DAS Sharing enables efficient network development by allowing several MNO to share a single network from the relay unit to antenna part. Furthermore, as sharing operators play the main role in installation, MNO has the advantage of not having trouble coordinating with building owners by themselves, but simply can install their base stations.
In JTOWER’s businesses, Indoor Infra-Sharing solution(IBS:In-Building-Solution)falls under the category of DAS sharing.
(4) Radio unit (RU) sharing
Radio unit (RU) is an important communication device for MNO that affects the coverage areas and quality of their networks. Until DAS sharing, each MNO installs radio unit that constitute the main elements of base stations. In RU sharing, however, each spectrum (allocated to each MNO) can be handled by a single radio unit.
For the next generation 5G and 6G, mobile phones system will become more sophisticated and the corresponding frequency bands will increase, so more efficient networking development will be required. Until now, there has been almost no RU sharing in Japan, but I believe that it is the area that sharing provider should approach.
In order to realize RU sharing, it is necessary to sufficiently verify that there is no communication issue with shared radio unit connected to MNO’s network and the difficulty level will be further increased.
In JTOWER’s businesses, we are developing 5G mmWave shared radio unit and it falls under the category of RU sharing. (As of August 1, 2023)
(5) Wireless network sharing (CU・DU)
In addition to RU sharing, wireless network sharing also shares a higher-level wireless network CU (central unit)・DU (distributed unit). Recently, the trend of network virtualization which uses software to control and manage wireless networks using standard server equipment has become remarkable. The introduction of network virtualization has the advantage of reducing equipment and other costs, as well as enhancing the flexibility of software.
I believe that sharing the entire wireless network in the context of this network virtualization will enable more efficient wireless networks development.
As the next step of wireless network sharing, there is a way in which the same spectrum is shared by MNO, but in Japan, the concepts of the spectrum sharing, such as who obtains licenses for radio stations, have yet to be resolved, so I am looking forward further discussion.
Is roaming between MNO the same as Infra-Sharing?
There may be some questions that roaming among MNO may also fall under the category of sharing. Roaming between MNO is a technique that has recently made KDDI network available to users of Rakuten Mobile. It is also attracting attention as a countermeasure for large-scale communication failures and disasters.
I believe roaming and Infra-Sharing do not belong to the same category.
Because main significance of roaming is to secure the temporary competitiveness of the new operator and protect users in emergencies. On the other hand, the purpose of Infra-Sharing is to pursue economic efficiency, so each initiative has a different concept.
High technological capabilities are required for each sharing provider
In this chapter, we have looked at the types of Infra-Sharing.
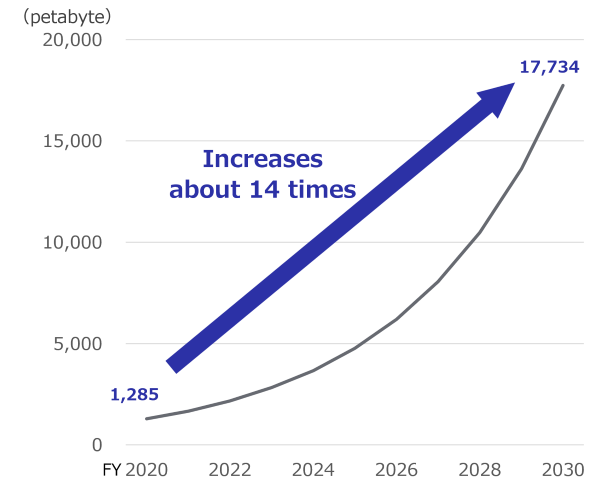
During the process of shifting to 5G and 6G, it is estimated that the data traffic will increase by 14 times. In order to handle the data traffic, it is necessary to quickly and efficiently install more base stations including for higher frequency bands.
I believe that each type of sharing listed so far will continue to be beneficial because of its respective usage and effect. Especially, under the categories where the sharing takes place within the wireless network ((4) RU sharing and (5) Wireless network sharing), I believe that it is most efficient to introduce Infra-Sharing prior to each MNO develop their own networks separately.
In providing Infra-Sharing services, sharing providers are required to develop equipment and have high technological capabilities that do not impair the communication quality provided by MNO.
The chapter 1 to 4 of this column is the introduction of Infra-Sharing.
In Japan, the growen of the Infra-Sharing market has become social demand and I feel, we are establishing a solid foundation.
In this business environment, I believe that the key drivers of the market will be the sharing providers who leverage their respective areas of expertise to create new value.
※The content in the article is at the time of publication.


