Infra-Sharing has multiple patterns. As the first part of this section, I will introduce 5 categories focusing on sharing levels. Then, explain about the categories unrelated to transmission and control parts of wireless communication networks.
The greater the range of sharing, the more efficient but difficult?
It is a bit conceptual, but first, let me sort situations by focusing on the range of sharing.
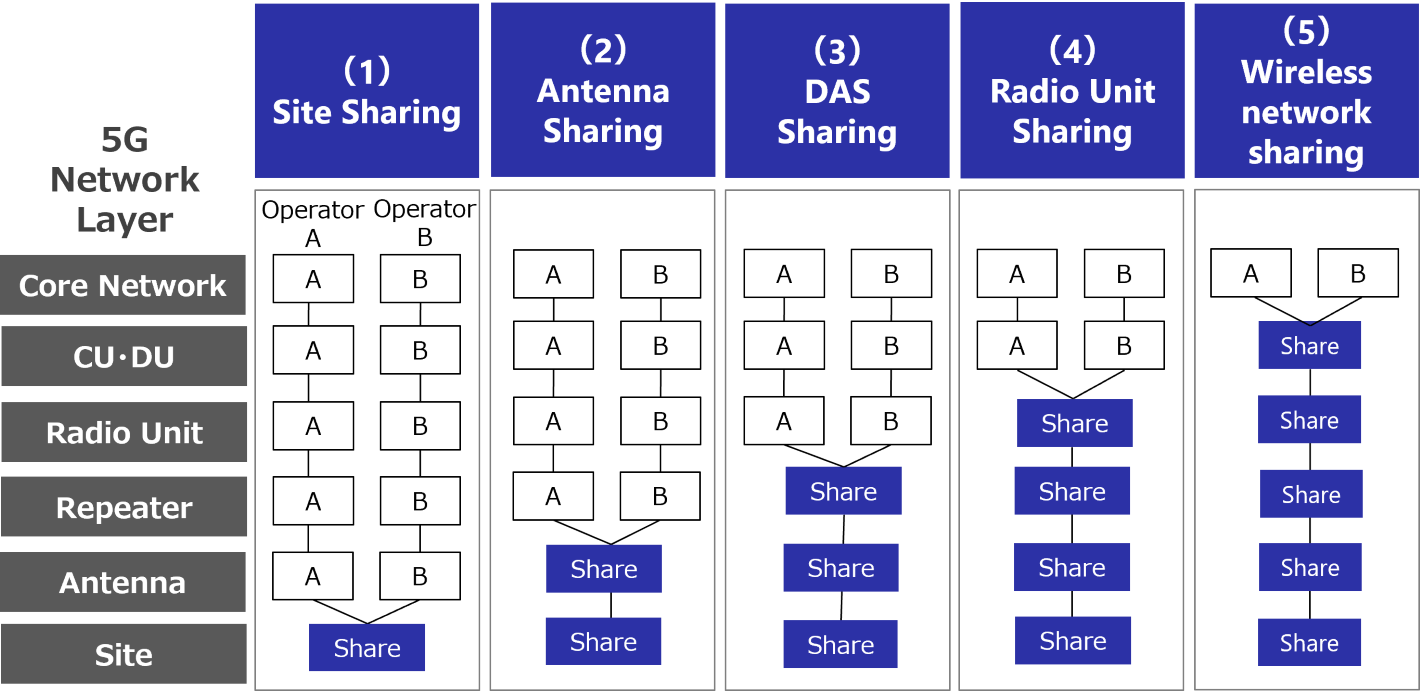
The image below shows the components of the mobile network and the range (1) to (5) are levels to be shared.
DU(Distributed Unit):Functional units for processing wireless signals and integration of RU
RU(Radio Unit):Functional units for controlling the transmission and reception of radio waves
From (1) to (5), the range of sharing is expanding. As the range is expanding, the reduction of CAPEX, OPEX and maintenance cost for MNO increases, as well as the reduction of electricity consumption and it will enable more efficient network development.
On the other hand, as the scope of sharing expands, it becomes interwined with the business policies of MNO, such as the selection of vendors for radio equipment and the network constructions including the installation of base stations. As a result, the implementation of the project becomes more challenging.
When the sharing provider introduces a new level of sharing, it is required not only to confirm the specifications and operation with each MNO, but also to secure a high level of service that is equal to the level provided by MNO. Furthermore, the key role of sharing provider is to coordinate projects ensuring that each MNO are equally beneficial through Infra-Sharing.
Let’s take a look at each sharing level.
Multiple towers are no longer necessary, and we can also anticipate enviromental benefits along with enhancements to the lundscape
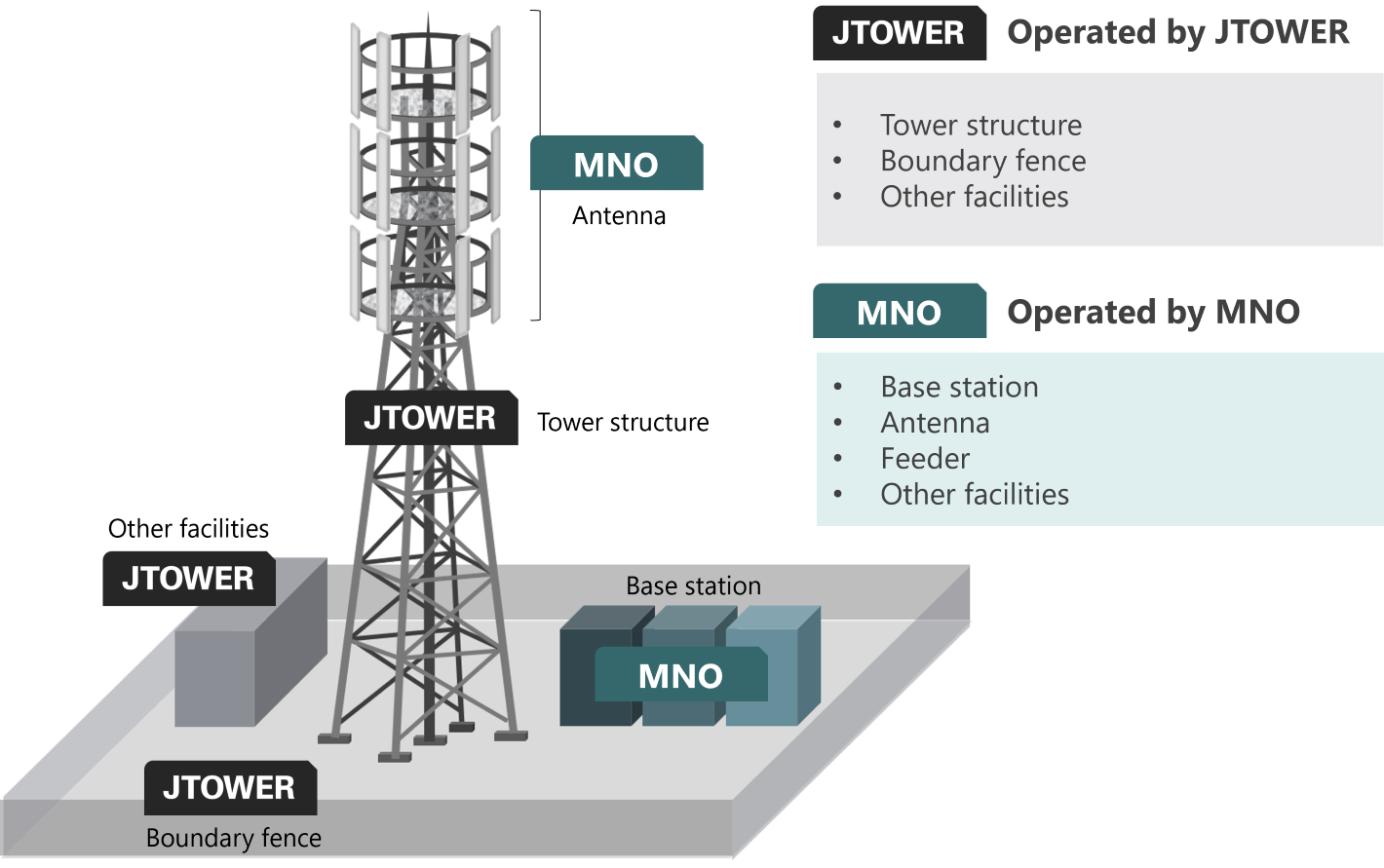
(1) Site sharing
Site sharing can be used when base stations are installed on the rooftop or when outdoor towers are built and base stations are installed. Sharing providers secure sites for base station installation and prepare towers, poles and shared facilities for the installation of antennas.
By utilizing the shared sites to install base stations, MNO will no longer need to search and negotiate for location and construct facilities. Outdoor in particular, there is no need to construct towers by each MNO, and in addition to improve environmental aspects, there are also benefits for landscape.
In JTOWER’s businesses, Carve-Out business (the purchase of existing towers from telecommunications companies) falls under the category of site sharing.

(2) Antenna sharing
In antenna sharing, in addition to site sharing, utilize the antenna prepared by the sharing operators. Antenna sharing can be also introduced when the base station is installed on the rooftops or outdoor towers.
The key difference from site sharing is that the antenna is also shared. This means that each MNO no longer needs to install its own antenna on the tower or pole, simplifying facilities, including the strength of towers and poles.
In JTOWER’s businesses, Rural tower sharing business, which constructs new towers as cell site and lease to MNO in the so-called geographically disadvantaged areas where the mobile coverage is not enough, falls under the category of antenna sharing.
Although this is a little extra, it is also necessary to procure power to install and operate base stations. In JTOWER’s rural tower sharing project, power-supply system for power procurement is also prepared by JTOWER and being used by MNO.

In the second part of this section, I will introduce the sharing levels related to wireless communication transmission and control.
※The content in the article is at the time of publication.


