In this column, I will introduce the entities that provide Infra-Sharing for mobile phone networks.
Recently, Infra-Sharing has been gaining significant attention, and as various industries have entered the market, a wide range of services has emerged, as discussed in the first column.
The Infra-Sharing providers highlighted here focus on offering parts of the mobile network or related services to multiple mobile network operators.
MNO driven and independent players
In introducing players that provide Infra-Sharing solutions, there are two major categories, MNO driven players and third-party (independent) players.
MNO driven players
1. Japan Mobile Communications Infrastructure Association (JMCIA)
- Established: September 27, 1994
- Membership: 26 companies (as of June 15, 2023)
The association is primarily operated by MNO and installs Infra-Sharing networks in the radio wave dead zones, such as road tunnels and railway tunnels as well as subway, underground malls and medical institutions. In addition, a part of the projects are being implemented through Radio Wave Shielding Measures, in which MIC subsidizes a part of the CAPEX.
The scope of the business is very broad and covers areas where mobile phones are used in large numbers, so the business itself is also heavily related to the quality of the mobile phone services.
2. 5G JAPAN
- Established: April, 2020
5G JAPAN was founded by two competing MNOs and it was epoch-making in Japanese mobile market. Although no detailed information has been disclosed on their business, we believe that the primary goal of establishing a joint venture is to promote the so-called hub function. This involves creating an environment where mobile facilities owned by each of Softbank and KDDI can be used with each other, rather than having new common facilities and operating them.
Third-party (independent) players
Third-party players have recently seen the entry from a variety of industries. First, I will categorize each business by its characteristics, and then further divide it into segments.
– Start Up –
1. JTOWER Inc.
- Established: June 15, 2012
JTOWER was established as an independent Infra-Sharing service provider.
When the company was founded, even the word of Infra-Sharing was not common in Japanese mobile market. Given that we were a start-up company and it was not easy to gain the understanding by MNO. However we have increased a track record from indoor Infra-Sharing and over the 10 years since our foundation, we have expanded our business including outdoor tower sharing, opening up the market for Infra-Sharing in Japan.
During the past 10 years, in addition to NTT (holding company), we have entered into equity alliances with NTT DOCOMO, KDDI and Rakuten Mobile to strengthen collaboration with MNO.
-Trading company –
2. Sharing Design
- Established: February 22, 2021
Sharing Design was established as a joint venture between Sumitomo Corporation (now SC5G, 100% owned subsidiary of Sumitomo Corporation) and Tokyu Corporation. Sumitomo Corporation has a track record in the domestic and overseas telecommunications business, including the cable televisions and leverage the value chain as a major trading company.
– Developer –
Developers and building owners have been entering Infra-Sharing market with a view to promoting the development of infrastructure for their properties. One of the characteristics of this segment is that it has a high degree of synergy with their existing businesses and can be directly linked to enhancing the customer’s value.
3. Mitsubishi Estate
- The company announced the launch of 5G Infra-Sharing business on January 26, 2022.
Mitsubishi Estate entered Infra-Sharing market by taking advantage of its strengths as a real estate developer that is skilled to increase the value of real estate. The company will promote deployment of 5G by supporting the shared use of facilities when installing 5G base stations on the rooftop. With the aim of increasing real estate value, Mitsubishi Estate expands targeted areas other than real estate owned and operated by the group.
4. East Japan Railway Company (JR East)
- On June 20, 2023, the company announced 5G areas coverage along railway lines by using Infra-Sharing.
JR East has traditionally built and operated commercial wireless communications networks, and has expertise in the field of wireless communications. By utilizing the knowledge and aiming to increase value for railway users, the company is promoting the early deployment of 5G by establishing common facilities on the premises of stations and between stations.
– Foreign affiliated company –
5. Tower Pods
- Established: January 15, 2020
The company was established as a subsidiary of the Lend Lease Group, a tower company operating mainly in Australia and will leverage the strengths as a tower company to expand the tower sharing business.
New value creation by third parties has become key to the market expansion
So far, I have introduced a variety of players that provide Infra-Sharing businesses. However, the size of Infra-Sharing market is still very small, compared to the scale of capital investment by MNO. Although no accurate market research has yet been conducted, Infra-Sharing is considered to account for less than a few percent of the annual CAPEX of 4 MNO, which amounts to over 2 trillion yen.
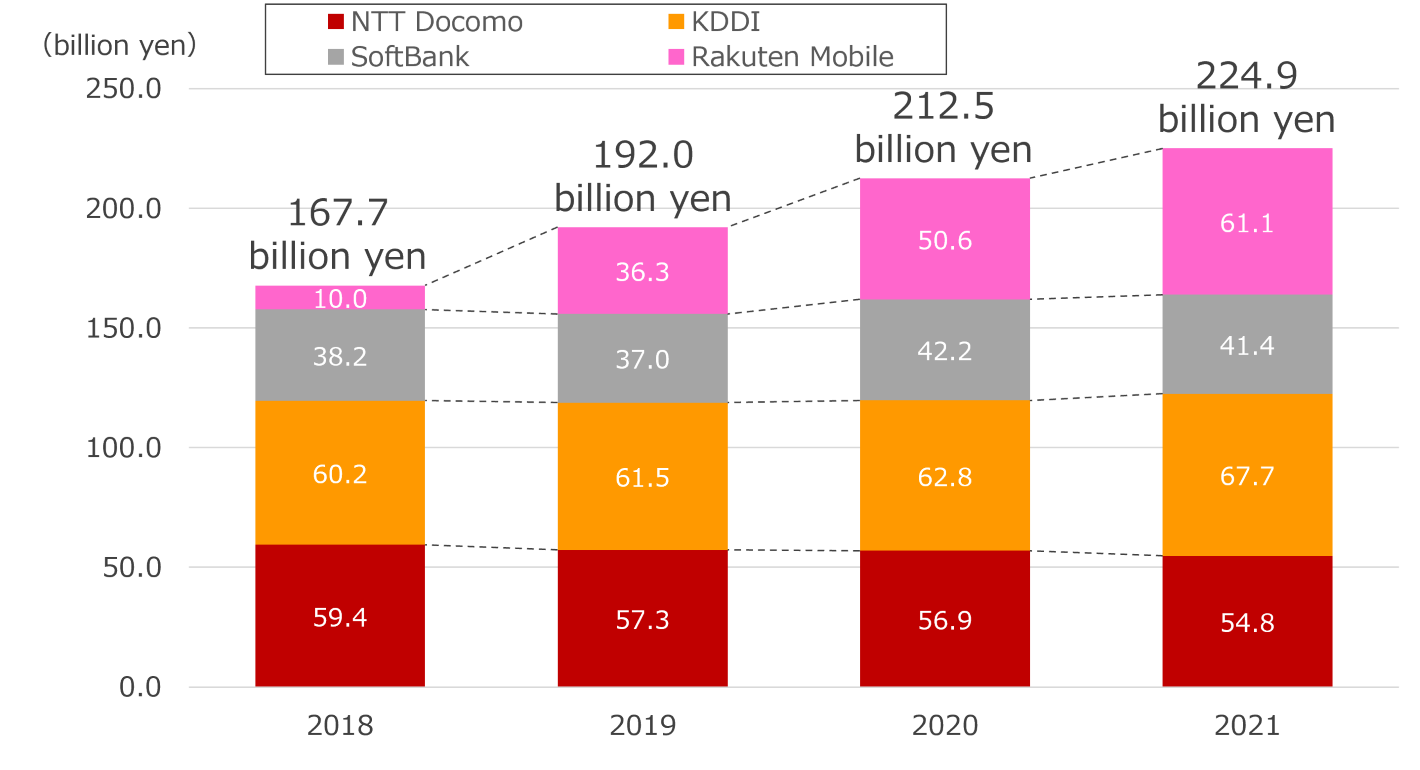
I believe that it will continue to be necessary to aim for market expansion while further fostering the social consensus on Infra-Sharing as an initiative to enhance the contributions of Infra-Sharing in the society.
※The content in the article is at the time of publication.


